Treatment For HIV Runs Low In U.S., Despite Diagnosis
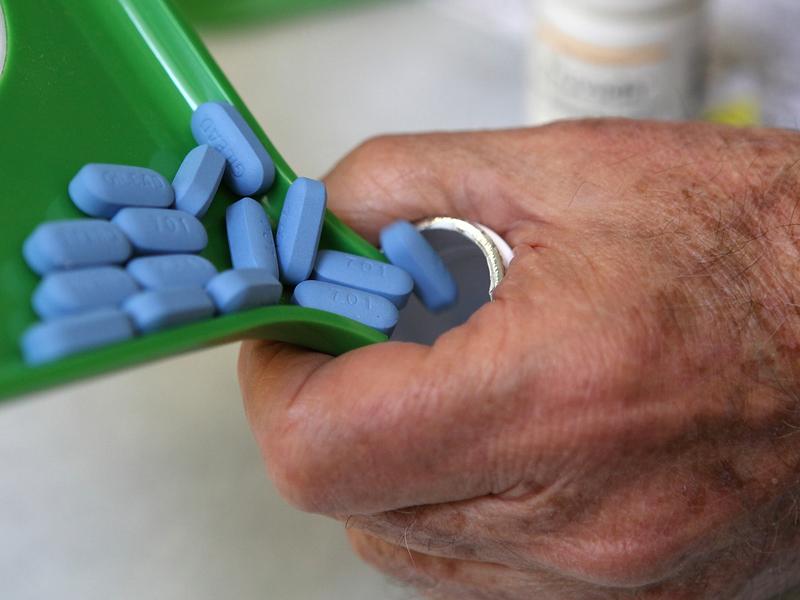
About two-thirds of Americans who are infected with the virus that causes AIDS aren't getting treated for it.
The finding comes from an analysis just released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showing that more needs to be done to make sure people infected with the human immunodeficiency virus get proper treatment.
"For people living with HIV, it's not just about knowing you're infected — it's also about going to the doctor for medical care," says CDC Director Dr. Tom Frieden.
The analysis, published in the latest issue of the CDC's Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, looked at nationwide data collected in 2011.
Of the 1.2 million people living with HIV in the United States, about 86 percent had been diagnosed and 40 percent were receiving some kind of medical care, according to the report.
Thirty-seven percent were prescribed antiviral drugs, which suppressed the virus for 30 percent of patients, the report said.
Antiviral drugs can help people who are HIV-positive to live years, sometimes decades, after they are infected. The drugs also reduce the chances they will spread the virus to someone else.
About two-thirds of those whose virus was out of control had been diagnosed but were no longer receiving care, the researchers found. That finding highlights the need to make sure people getting treated for HIV continue to receive care, Frieden says.
Young HIV-positive people were especially unlikely to have their infection under control, the researchers found. That's probably because younger people are the least likely to know they are infected.
9(MDEwODYxNTQyMDEzNjAxODk2Nzc2NzNmYQ001))